Charging stations use electricity to charge your electric car, that is evident. But this power is not always expensive or sufficiently available at all times. That is why it is important to use this energy efficiently. Especially if, in the future, we will generate power using only renewable energy sources such as wind and solar power. There are several ways to distribute power properly, including peak shaving and peak shifting. What does this actually mean?
What are energy peaks?
Before we start with a detailed explanation of peak shaving and peak shifting, it is important to understand exactly what energy peaks are and why we want to avoid them.
Energy peaks are times when electricity consumption increases suddenly and significantly above average levels. These peaks can occur at different times of the day, depending on the behaviour of consumers and businesses. Typical examples of energy peaks are:
Morning hours (6-8am): When people get up, shower, make coffee and switch on electrical appliances in the house.
Evening hours (21-23h): When people come home from work, cook, turn on television and charge their devices.
Why do we want to avoid energy peaks?
Avoiding energy spikes is important for several reasons.
Load on the power grid: During energy peaks, the power grid is heavily loaded, as a huge amount of power has to be supplied in a short period of time. This can lead to overloading of the grid, increasing the likelihood of breakdowns and blackouts. Grid operators e.g. Fluvius then have to construct extra infrastruture to handle these peak loads, which is expensive.
Higher energy costs: During peak hours, electricity is often more expensive because it is more difficult and expensive for energy suppliers to meet demand. Then they sometimes have to use less efficient energy methods to meet the increased demand.
Environmental impact: Energy peaks require switching on additional power plants, which often use fossil fuels such as gas or oil. These power plants emit more CO₂ and other pollutants, contributing to air pollution and climate change. By reducing energy peaks, we can reduce our carbon footprint.
What is peak shaving?
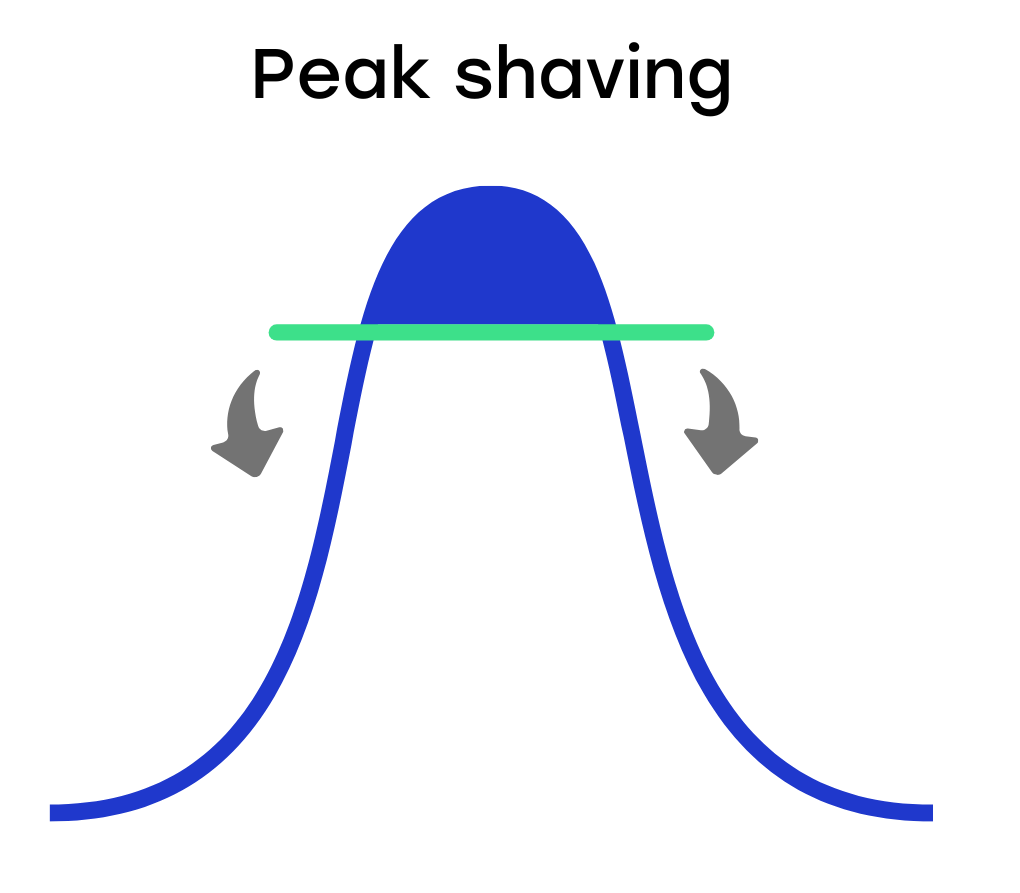
Peak shaving is certainly not exclusive to charging stations and electric cars. It is a term that has been around for a long time, but mainly large industrial companies used it. Since the rollout of electric driving, smaller companies and ordinary consumers have also come across the term.
With peak shaving, the large energy peaks are smoothed by using previously stored energy. If you look at the energy peak in in the illustration above, you can see that it exactly wears a 'hat'. We don't want this hat, and peak shaving takes care of that.
Some days, in fact, more energy is generated than is needed. Instead of letting that energy go, we capture it in a storage facility. This allows us to deploy it cleverly at times when there is just a lot of demand for energy, but not enough supply.
One way to do this is to install large batteries at companies, for example, that store energy from e.g. solar panels on the roof of the factory. But this can also be done just at your home these days!
You then set a maximum capacity for your charging station. The charging station then continues to charge, but once the energy peak becomes too high, the charging station automatically switches to a lower capacity or another energy source takes over (e.g. the solar panels on your roof). This prevents you from exceeding the maximum power capacity of your home.
What is peak shifting?
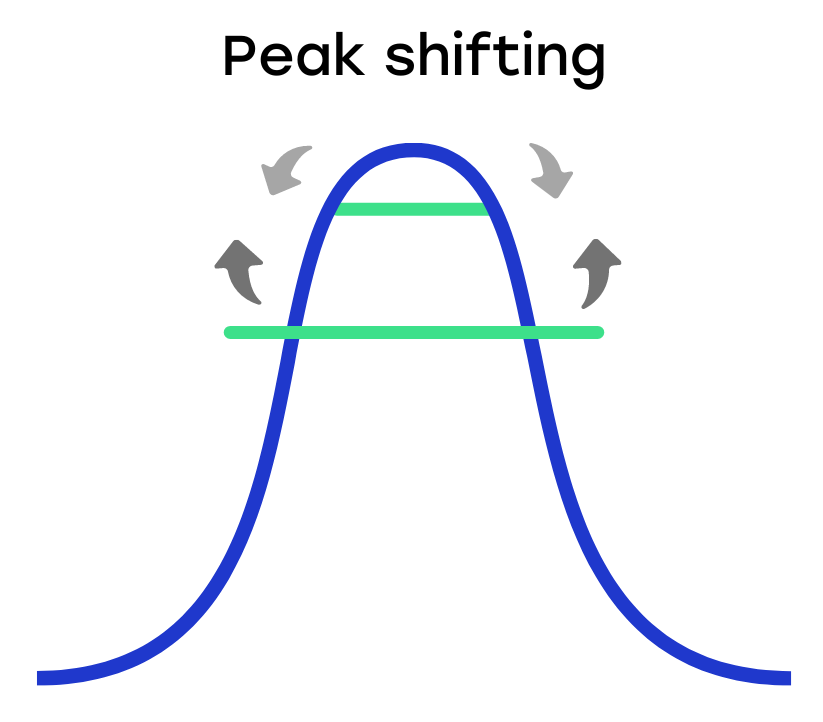
So in peak shaving, you prevent a peak in energy by completely smoothing it out. With peak shifting, this is not the case. The amount of energy you consume remains the same, but it is shifted to other hours.
Peak or load shifting revolves around shifting energy consumption to times when electricity demand is lower, often referred to as 'off-peak' hours. This is done by charging when electricity is cheaper and more widely available, such as in the middle of the night. Peak shifting not only helps to reduce energy costs, but it also relieves the electricity grid during peak hours.
For example, instead of charging the electric car immediately after returning home in the evening, you can use peak shifting to set it to start charging only after midnight, when power demand is lower.
The benefits of peak shaving and peak shifting
Lower energy costs: By reducing power surges, you save on your energy bill..
Less load on the power grid: By optimising your charging behaviour, you help to relieve the load on the power grid.
How can you apply peak shaving and shifting?
You can effectively set peak shaving and peak shifting modules on a smart charging station. Smart charging stations are equipped with technologies that allow you to implement such modules that help you optimise your charging behaviour and reduce power spikes.

Alfen Eve Single Pro
The Eve Single Pro-line is a smart charging solution and is suitable for private and semi-public locations.

Zaptec Pro
The Zaptec Pro is a smart and efficient charging device for large parking lots of residences, businesses or new construction projects.
The difference between peak shifting and load balancing
You may have heard of the term load balancing when researching charging stations and electric charging. But this is not to be confused with peak shifting; these are two separate technologies.
Peak shifting revolves around shifting energy consumption to times when electricity demand is lower, often referred to as 'off-peak' hours.
Load balancing, on the other hand, is about evenly distributing the available power across multiple charge points at one specific location. The aim is to prevent the total power demand from exceeding the capacity of the grid at that location. This is especially important in places where multiple vehicles are charged at the same time, such as in offices or flat blocks.
Imagine a company has a car park with ten charging stations. If all these charging stations operate at full capacity at the same time, this could lead to overloading the local power grid. Load balancing ensures that the power available is evenly distributed among the ten charging stations, so that each vehicle is efficiently charged without exceeding the maximum grid capacity.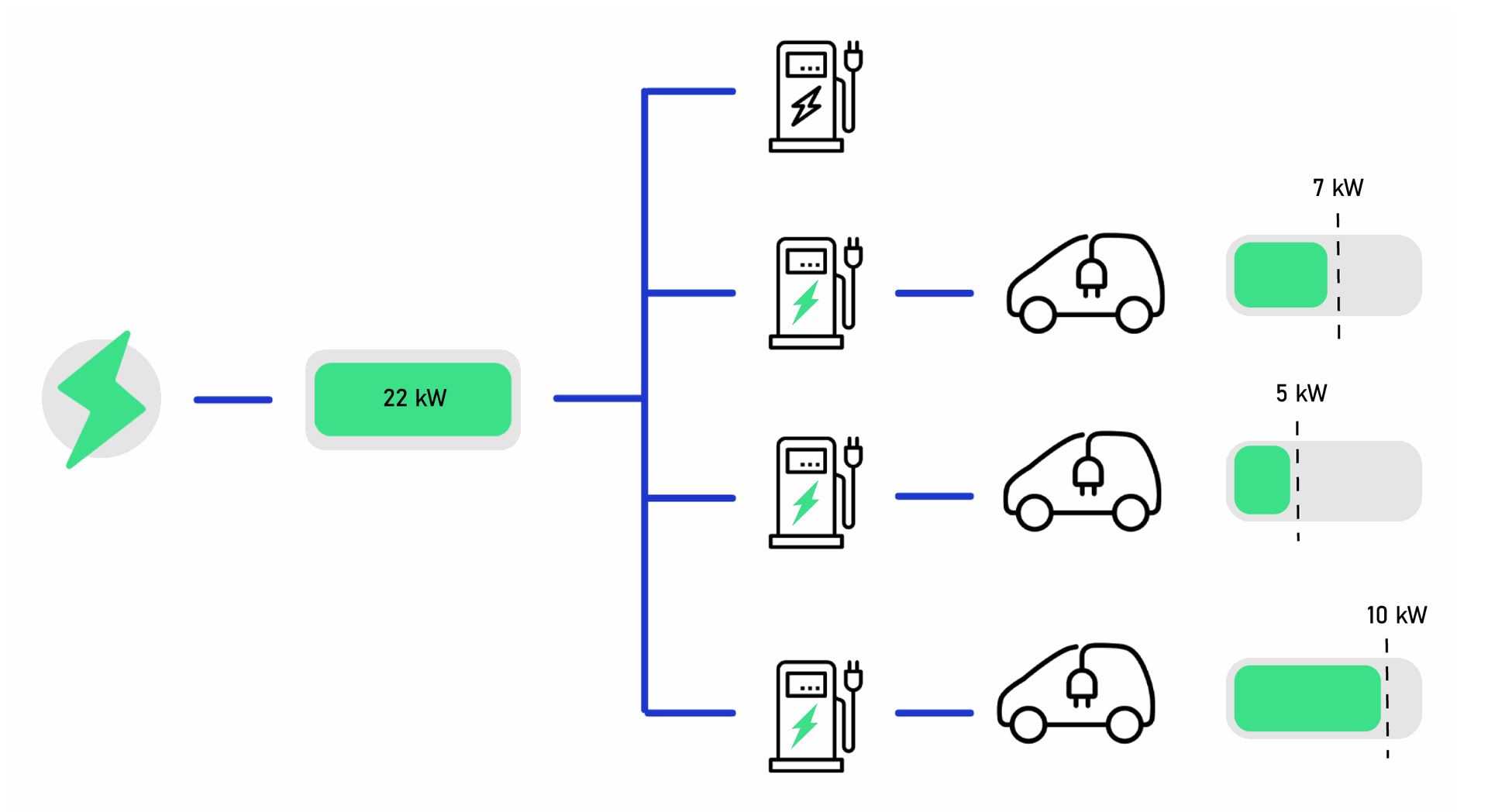
Summary of differences
Peak shifting: Shifts energy consumption to times of lower demand, reducing energy costs and relieving the grid during peak hours. The aim is to use energy when it is cheapest and most available.
Load balancing: distributes the available power evenly across multiple charging points, preventing overloading of the local grid. The aim is to make efficient use of available power without peak load.
Why are both important?
Both peak shifting and load balancing are important for an efficient and sustainable energy infrastructure:
Peak shifting helps reduce energy costs and contributes to a more stable grid by spreading consumption.
Load balancing allows multiple vehicles to be charged simultaneously without overloading the local power grid.
The future of electric driving and renewable energy is closely linked to how efficiently we can integrate these technologies. Innovations such as peak shaving and peak shifting will play a major role.
